RUMA is a media analysis platform focused on amalgamating and interrogating news items extracted from search engine results pages. The sophistication of algorithms used by Google and others to rank news today means the results they deliver for a given search are a good approximation of what people are actually reading. In some ways, if the news isn’t ranked in a Google search, it might as well not exist.
With that in mind, a media analysis based on news indexed and ranked by Google can deliver a more accurate view of news reach and traction than an analysis of all available news. Why? Because Google tends not to rank pages that few visit e.g. press release reprints and inclusions in news aggregator sites.
RUMA allows you to simultaneously interrogate the Google News results for up to ten different search terms (company names, technologies, issues etc.). The application will download up to 400 results for each search term (in practice, Google never gives more than 400 results for news searches).
News analysis
- In addition to the basic search terms additional parameters can be defined:
- The dates the want the results for e.g. 01/01/2021 to 31/12/2021
- The country you want the search results for i.e. do you want to see the results a user in the US would see rather than those a user in the UK would see (they will be different).
- The language of the user you want to replicate i.e. a user in Belgium might be using French, English or Dutch. Once again, they will all receive different results.
- The results of the searches will be presented in a table with links to the articles in question and they will automatically be analysed to produce a series of charts (articles per title, articles by date, results per search term and the languages used in the top 20 articles of each search term).
- You have the ability to exclude entire sources (titles/domains) from the charts or to exclude individual articles.
- Raw results can be downloaded and opened in a spreadsheet.
Domain analysis
- The domain analysis element allows you to search up to five specific domains (e.g. techradar.com, bbc.co.uk etc.) for up to five search terms. It will then download a summary of every article (max 400) the domain has published that Google has classified as news (regardless of how well it ranked).
- The interactive chart will allow you to compare, for instance, how many articles your client/company received in those titles (domains) vs a range of competitors.
News Analysis - examples
Comparing the ranking news coverage of a series of companies within specified dates
The application does not gather every piece of news that may have been written about the companies in question. It gathers what Google’s algorithms have assessed to be the highest ranking news within the period specified. It’s important to understand this point when presenting and interpreting the results. For instance if you are comparing two significant companies over a long time period, Google will likely return a similar number of results for both, simply because of the overall volume of news they produce. In contrast, for smaller companies and/or shorter time periods, the results can give a decent approximation of relative (rather than absolute) media traction.Comparing currently ranking news for a series of companies
Unlike the example above, if no dates are specified , the application will gather the current ranking news for the companies specified. Once again, larger companies typically have significant news output so the absolute volume of ranking news will be similar but if you are looking at smaller companies, you may find significant differences in volume which will give you an indication of relative traction.Examining ranking coverage for a series of topics/issues etc.
In the same way as you compare coverage of companies you can compare coverage of topics/issues etc. This is very useful to establish which titles publish content on those topics/issues that consistently ranks well in Google News.Comparing volume of ranking coverage in specific titles
The application analyses the data downloaded and presents a graph showing the top 40 titles by volume of ranking articles. This graph can be used to put together a shortlist of titles you may want to target. Additionally, if you are comparing companies, it will indicate whether one company is getting significantly more traction in a title than another.Examining peaks and troughs
A graph is provided that plots volume of articles, for each search term, over time. This allows you to see the peaks and troughs of ranking coverage.Geographic variations
RUMA allows you to replicate the experience of someone searching Google News in any country. For instance, you may be interested to see if a particular company is getting traction in the UK versus the USA. To do that you would set up a two simultaneous searches, one for the company in the UK and one in the USA and then compare the results in the charts provided.Language analysis
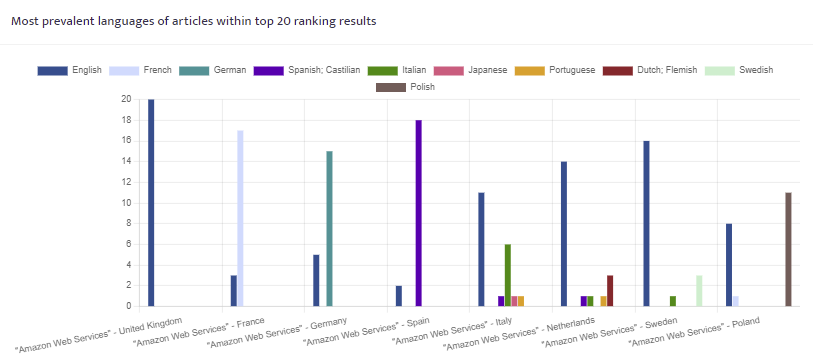
The application examines the text of each of the top 20 ranking articles to establish what language they are written in, and presents the results in a graph. This data can be used for fundamental campaign design. For instance, if the majority of the top ranking articles for a particular topic/issue in France, Spain, The Netherlands and Norway are actually in English, you may conclude that an English language campaign would return a greater return on investment rather than spending the available budget trying to engage with titles operating in French, Spanish, Dutch and Norwegian.
Domain analysis
The domain analysis element has a very specific application. It allows you to define up to five search terms (companies, topics, issues etc.) and search up to five specific domains (e.g. techradar.com, computing.co.uk, bbc.co.uk etc.) for all articles in those domains (max. 400) that Google has classified as news within a given time period.
This is a very useful element to establish absolute traction for the search terms of interest in the media titles you are most interested in.
Defining the search parameters
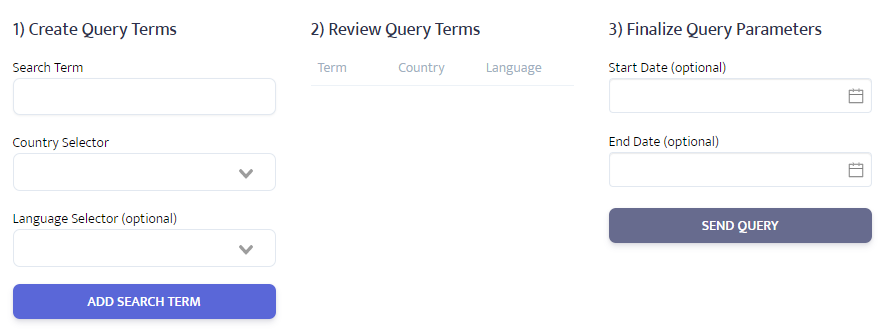
- Enter the first search term, the country from which you wish to search and, optionally, the language of the user you wish to replicate. If no language is selected, the application will default to the most common language used in the country specified. Click ‘ADD SEARCH TERM’ and repeat for each search term (up to 10). NB. In 'Search Term' field you can use any of Google's advance search operators to refine the results you receive.
- Enter the dates you are interested in or leave blank for current ranking results
- Click ‘SEND QUERY’
Reviewing the results
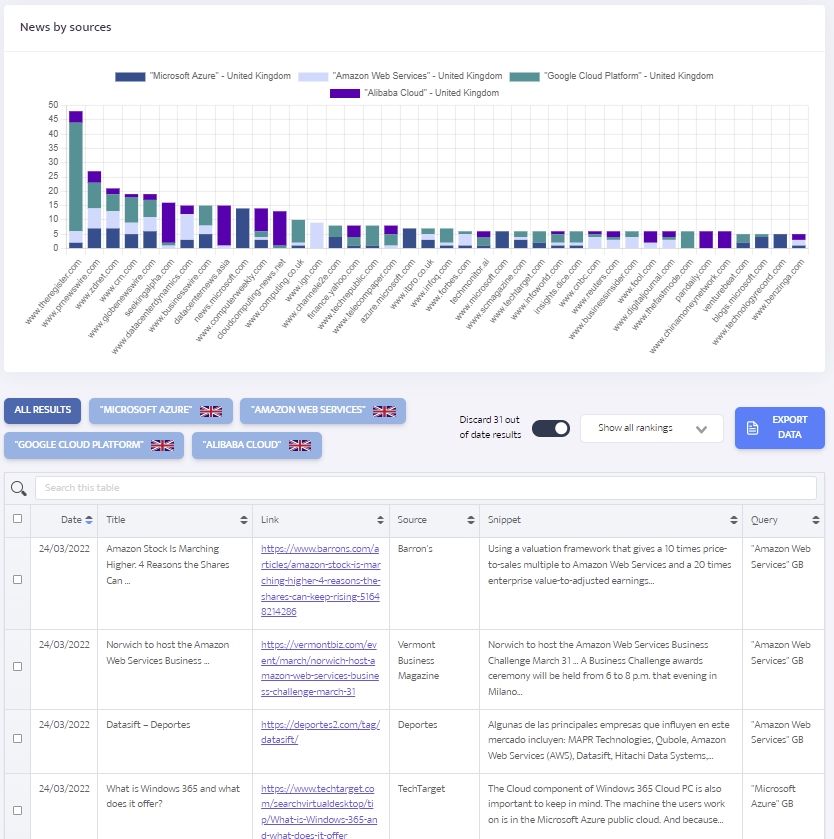 After the data loads you will be presented with a chart showing the top 40 titles ranked by volume of ranking articles. This chart is interactive – clicking on the search terms in the legend will exclude results from that search term from the chart.
After the data loads you will be presented with a chart showing the top 40 titles ranked by volume of ranking articles. This chart is interactive – clicking on the search terms in the legend will exclude results from that search term from the chart.
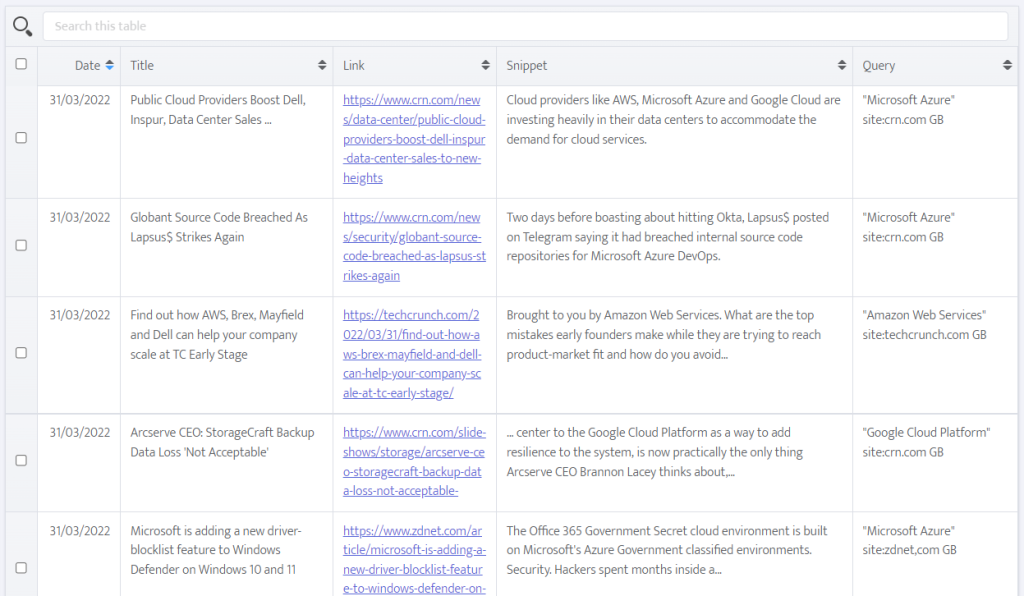
The first of tabs below the chart (‘ALL RESULTS) shows an amalgamated list whereas the other tabs will show only those results for the search terms you have used. The 'All results' tab is initially sorted in date order without rank position whereas the tabs of the individual search results show ranking data are initially sorted according to rank. The results can be sorted differently, e.g. by source, by clicking on the relevant column header.
When the ALL RESULTS tab is active, clicking on any of the articles shown will bring up two buttons which will allow you to exclude (or include if previously excluded) all articles from the domain that article was found in. The chart will update accordingly e.g. you might wish to exclude all articles from newswire domains.
When any of the search term tabs are active, clicking on an article will bring up two buttons that will allow you to exclude or include that specific article e.g. because it’s not relevant to your analysis.
Sometimes Google will deliver results that are outside of the dates you have specified. This typically happens when there aren’t a large number of results for the search/es in question. If you wish to exclude those out of date results a toggle switch is provided.
You can also download the results in the from of a ‘comma separated values’ (CSV) file which can be opened in a spreadsheet if you wish to do some analysis outside of the app.
Charts
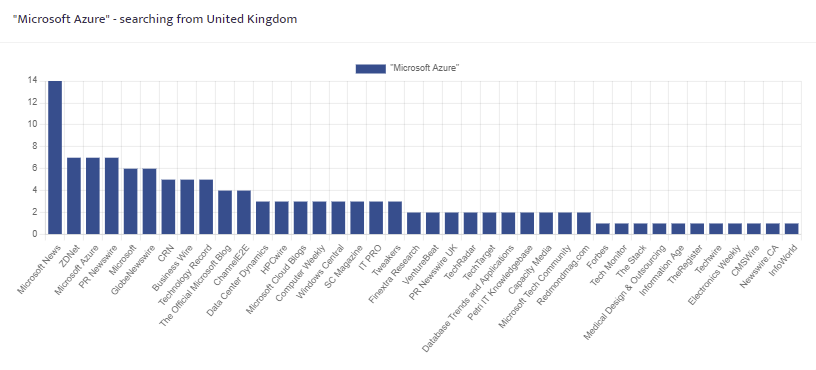
Articles per search
Individual charts for each search term showing the top 40 titles measures by volume of articles within the search results.
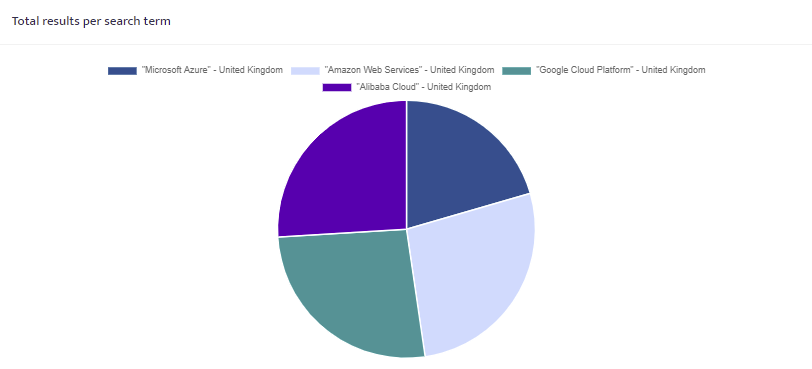
Total results per search term
A pie chart showing the total number of ranking search results for each of the search terms defined
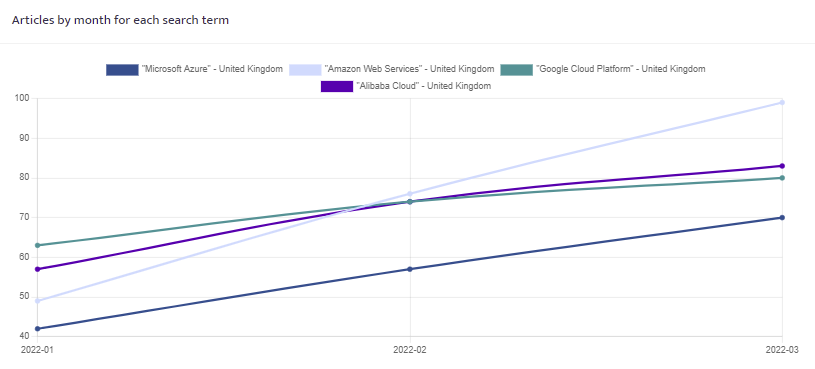
Articles by date
A chart showing the total number of articles in each month, for each of the search terms defined.
Language analysis
The app analyses the first twenty articles of each result to establish what language is being used and presents the data for each search term.
NB. All charts are interactive and may be copied by right clicking and selecting ‘save image’.
Defining the search parameters
Defining the terms for the domain analysis is similar to the news analysis. First add each 'Query term' by entering the term and clicking 'Add term'. Secondly, add each domain (e.g. techcrunch.com) in the domain field, select the country from which you want to replicate the search, and click 'Add domain'. Up to five queries and five domains may be added. If you want to restrict the results to those published between specific dates, enter the dates required. Finally, when queries, domains and dates have been entered, click ‘FETCH RESULTS’.

Reviewing the results
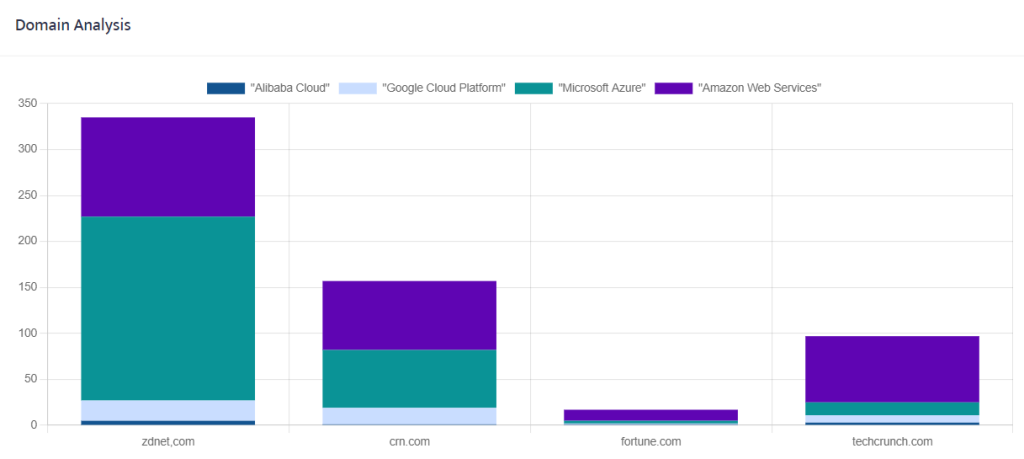
The domain analysis chart is fully interactive – search terms and/or domains can be excluded or included dynamically.
The raw results of the defined searches are displayed below the chart and, as per the main news analysis, each individual article can be excluded or included.
Depending on the RUMA package you have purchased, you will be allocated a fixed number of credits per month/year. One credit is equivalent to a single page of up to 100 Google News results (the maximum number Google will currently deliver on one page). RUMA will deliver a maximum of 400 results per search term.
You can estimate your use of credits using the following formulas:
News Analysis
Number of search terms
x
(up to) 4
=
Credits used
e.g. four search terms with between 300 to 400 results each would represent 16 credits (4 x 4 = 16).
Domain Analysis
Number of search terms
x
Number of domains
x
(up to) 4
=
Credits used
e.g. Searching for two terms across two domains with between 200 to 300 results each would equate to 12 credits (2 x 2 x 3 = 12).
Void searches
A search that is submitted but which produces no results (i.e. Google cannot find anything relevant) equates to a single credit.

